Temporal Demultiplexing
With temporal demultiplexing, ScanImage can associate the measured fluorescence to its excitatory pulse by time using virtual channels. Virtual channels can then be assigned color and spatial information so they are displayed distinctly and in appropriate places.
With application of optics, it is possible to split laser pulses and distibute them spatially in the sample with each subdivision of the original pulse exciting the sample at a different time.
Some applications for this are:
Prerequisite
To make use of this feature, you will need an optical system which can make particular use of this feature. MBF Bioscience offers a solution called vCAm which distributes subdivided light pulses into up to 15 depths of adjustable uniform spacing, which are raster scanned simultaneously such that the frame rate of the raster scan is now a volumetric rate.
Another prerequisite is that acquisition of samples must be synchronized to the laser repetition rate to associate fluorescence to a duration offset from the time of the last laser pulse. To synchronize acquisition, follow the Synchronization to Laser Clock tutorial.
Tutorial
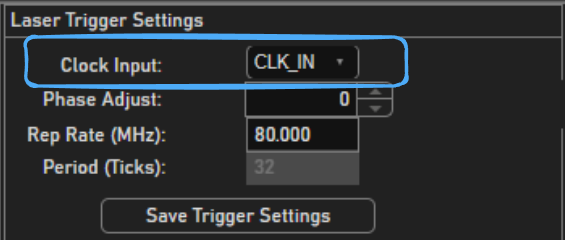
Set the
Clock Inputfrom the Laser Trigger Settings toCLK IN.
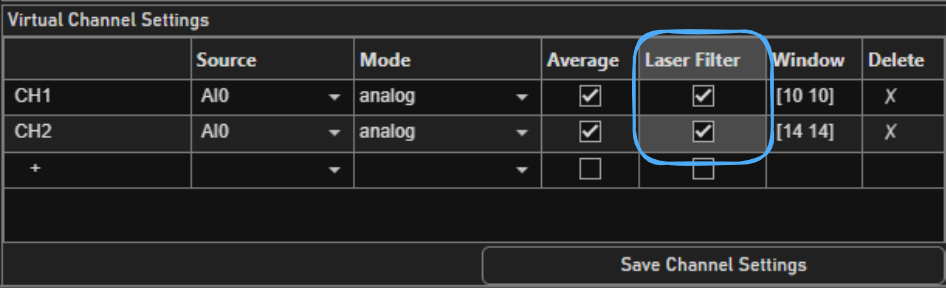
Enable laser gating on virtual channels where this technique should be leveraged.
Acquire data by clicking
Start Scopeand starting aFocusacquisition

Tip
when first aligning channels in time with windows, it is helpful to use a fluorescent slide
such that all light beads produce fluorescence. Later when imaging actual fluorophores of interest,
The phase of the collected signal relative to the windows can be shifted using the Phase Shift
editable text box in the Laser Trigger Settings panel.
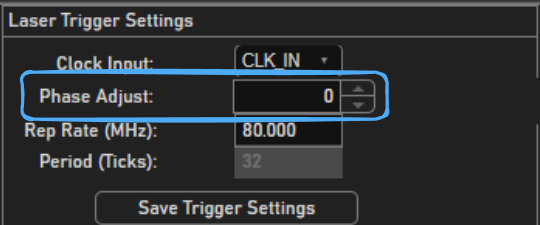
Offset the signal in time to ideally be subdivided into channels by time Windows using the
Phase Shifteditable text box. Best to offset collected peaks for the last sample between laser pulses.
Offset temporal windows of the virtual channels so that they overlap with fluorescent peaks.
(Optional) Associate virtual channels with relative depths in the sample