I2C data recording
Note
This is a premium feature that is available with vDAQ (RggScan) or resonant scanning with National Instruments hardware (ResScan) only.
I2C is a simple two wire serial bus. To synchronize a behavioral experiment with imaging, ScanImage® can act as a I2C bus slave. When an event occurs, the controller of the behavioral experiment can send data bytes to ScanImage. ScanImage® will timestamp the incoming packet and log the data bytes to the Tiff header of the appropriate image frame. To learn more about the I2C protocol, review the I2C Wikipedia article.
Note
This feature is supported for both resonant and linear scanning when using vDAQ. When using NI hardware platform, this feature is supported in resonant scanning (ResScan) only.
Wiring
The I2C bus is directly monitored by the ScanImage® FPGA. The I2C bus requires both the Serial Data Line (SDA) and Serial Clock Line (SCL) to be “pulled” to VDD through pull-up resistors. For this purpose, +5V output on the breakout can serve as VDD. To calculate a resistance value for the pull-up resistors, please review this resource.
Regardless of DAQ hardware, the following points should be observed: - Devices sharing the bus should also share a common ground with the DAQ.
Less often is this relevant, but also of note:
Note
I2C devices use open-drain terminals for SDA and SCL. This means they can only pull the bus lines to low, but rely on the pull up resistors to reset the lines to VDD. If a device is used to emulate an I2C master that can actively drive the bus (i.e. a NI-DAQ board), no pull-up resistors are required.
vDAQ
Bus line |
vDAQ Channel |
SDA |
Any channel in group 0, 1, or 2 |
SCL |
Any channel in group 0, 1, or 2 |
GND |
Ground paired with SDA and SCL lines via BNC. |
VDD |
+5V |
Note
When “ack” (acknowledge) output is enabled (see below) SDA must be in digital group 0 or 1
NI ResScan
When using NI hardware, the NI SCB-19 breakout box is required to connect the bus to the FPGA.
Bus line |
SCB-19 Pin |
SDA |
PFI0 |
SCL |
PFI1 |
GND |
GND |
VDD |
+5V |
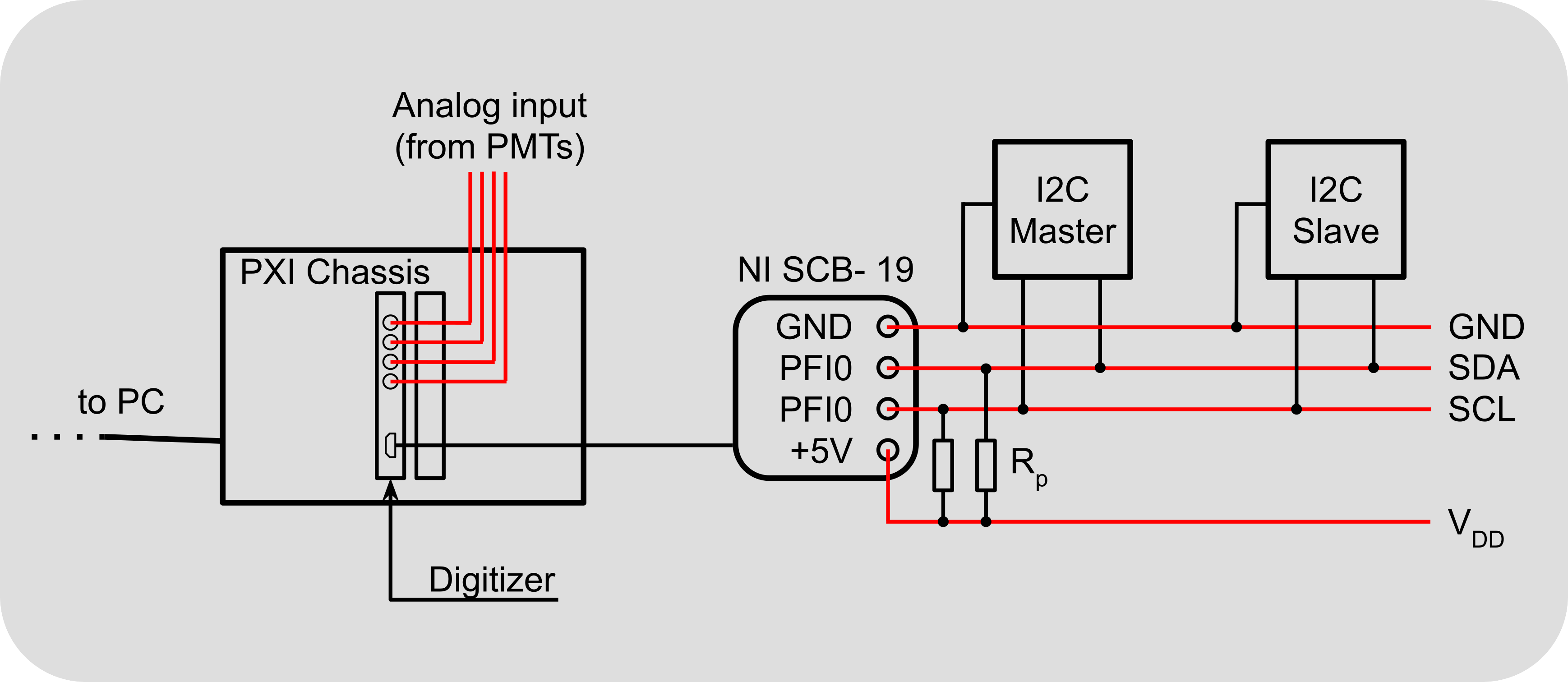
I2C wiring
Sample wiring diagram for ScanImage® as I2C slave. SDA and SCL are pulled to VDD via pull up resistors Rp.
Software
For the vDAQ, I2C can be configured from the vDAQ Imaging System page on the I2C settings tab:
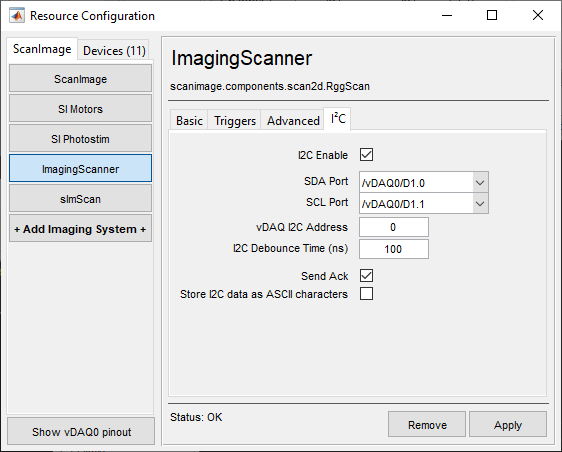
Otherwise, one can edit the machine data file to configure I2C in ScanImage. To configure ScanImage® as an I2C slave, add the following lines to the ‘ResScan’ section of the Machine Data File:
1%% ResScan
2
3...
4
5% auxTriggering, photonCounting and I2C are mutually exclusive features
6auxTriggersEnable = false; % disable auxTriggersEnable so that I2C can be used
7photonCountingEnable = false; % disable photonCountingEnable so that I2C can be used
8
9I2CEnable = true % enable I2C slave capability of FPGA
10I2CAddress = uint8(0); % [byte, 0-127] configures the I2C address of the FPGA
11I2CDebounce = 500e-9; % [s] time the I2C signal has to be stable before a change is registered
12I2CStoreAsChar = false; % if false, the I2C packet bytes are stored as a uint8 array. if true, the I2C packet bytes are stored as a string.
13% Note:a Null byte in the packet terminates the string
14I2CDisableAckOutput = false; % the FPGA confirms each packet with an ACK bit by actively pulling down the SDA line. I2CDisableAckOutput = true disables the FPGA output
I2C packet format

I2C sample packet
Sample of an I2C data package sent by the I2C master to an I2C slave. The transmission starts when the master pulls SDA to low while SCL is high. The master generates the clock and the ScanImage® FPGA samples SDA on the rising edge of SCL. SDA needs to remain at a stable logic level for the entire duration of SCL high. The first byte sent by the master is the address of the slave. The following bytes are data bytes. The slave confirms receiving the byte by pulling SDA to low after the last bit in the byte. At the end of the transmission or if the transmission fails, the master releases SDA while SCL is high.
Note
On the I2C bus a byte is transmitted with the most significant bit first.
Data format
ScanImage® saves received packets in the Tiff header of the appropriate image frame. When a start of packet signal is registered on the I2C bus, the FPGA generates a high precision time stamp which is saved with the data to the frame header. Depending on the Machine Data File setting ‘I2CStoreAsChar’ ScanImage® stores the packet either as ‘binary’ byte array (each byte is a value of 0-255) or as string. If saved as a string, a received byte of value 0 is interpreted as the end of string.
Tiff frame header for I2CStoreAsChar = false
I2C = {{timestampPacket1, [byte1 byte2 ... byteN ]} ...{timestampPacketN, [byte1 byte2 ... byteN ]}}
Tiff frame header for I2CStoreAsChar = true
I2C = {{timestampPacket1, 'my data 1'} ... {timestampPacketN, 'my data 2'}}
Emulate I2C master using a NI-DAQ board
A Matlab example using an NI-DAQ board as an I2C master can be downloaded here.
Note
At the end of each transmitted byte, the I2C master and slave switch roles. To acknowledge the successful transmission of one byte, the I2C slaves pulls SDA to low during one SCL clock cycle.
If a NI-DAQ board is used to emulate an I2C master, this output can be deactivated so that ScanImage® never actively drives SDA. This can reduce the risk of short circuit. To deactivate the ACK output, set the following parameter in the Machine Data File:
I2CDisableAckOutput = true;